A high-security industrial site in Russia, previously kept under wraps, is now drawing international attention due to a significant and rapid transformation. Recent satellite imagery reveals major expansion efforts at a facility believed to be central to the country’s drone manufacturing program, while Russian officials have simultaneously allowed a rare look inside the plant—a move that has raised eyebrows among defense analysts and geopolitical observers.
The location, situated within the Alabuga Special Economic Zone in the Republic of Tatarstan, seems to be experiencing significant growth. Recent satellite images with high-resolution detail display increased construction efforts throughout the last year. New structures, improved infrastructure, and what seems to be improved logistical capabilities are now observable from an aerial perspective. These developments imply considerable financial investment aimed at increasing the production of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), probably to meet the shifting requirements of Russia’s current military activities.
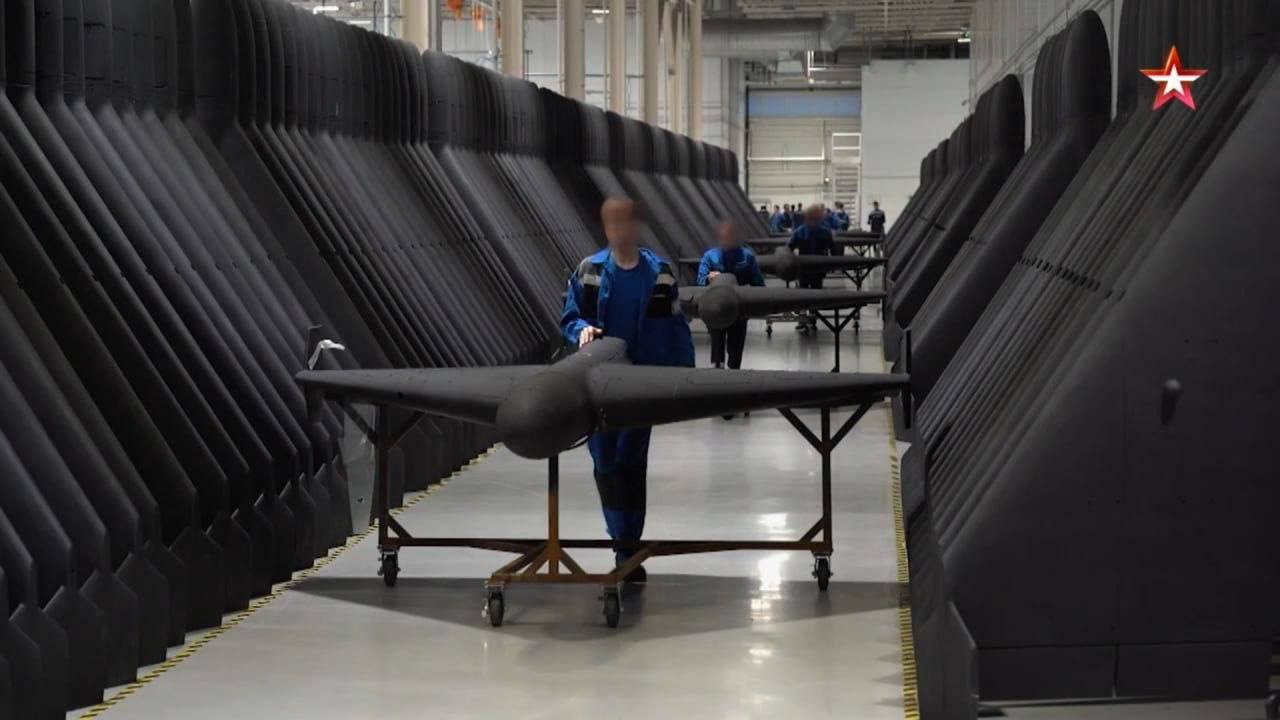
Although satellite monitoring has provided a perspective on the progress, Russia has done something uncommon by revealing aspects of its drone production process. State-run media channels have recently broadcasted scenes from within the factory, highlighting assembly lines, parts, and workers in action. Despite being carefully managed and likely designed to align with strategic communication objectives, the footage represented an unusual moment of openness for an industry typically enveloped in confidentiality.
This dual unveiling—both through independent observation and government-sanctioned media—highlights the increasing strategic value Moscow places on drone capabilities. Unmanned systems have become a key element in modern warfare, used for reconnaissance, targeting, and offensive strikes. Their utility in conflict zones, including Ukraine and beyond, has led to intensified focus on production and technological development within the defense sector.
Defense specialists reviewing the satellite photos identify several signs of rapid growth. Among the most prominent are the emergence of new buildings that resemble production facilities or storage spaces, the expansion of transport routes, and the setup of support systems, including electrical and communication networks. Collectively, these components suggest a shift towards increased production capacity and enhanced operational independence.
The site’s location within a Special Economic Zone offers advantages such as tax incentives, streamlined logistics, and reduced oversight, all of which can contribute to faster development timelines. These zones are designed to attract investment and innovation, and in this case, appear to be serving a dual purpose by supporting military-industrial growth.
Russia’s decision to showcase the facility may be partly intended to send a message—both domestically and internationally. On one hand, it suggests confidence in the country’s manufacturing capabilities and a desire to project resilience despite sanctions and export controls. On the other, it may aim to influence perceptions of technological parity or superiority, especially in the context of ongoing geopolitical tensions and defense posturing.
Analysts point out that the facility seems to prioritize the construction of UAV systems that have been commonly used in recent conflicts. This encompasses loitering munitions—drones intended to remain over a target site prior to striking—and reconnaissance variants. Some sources indicate that manufacturing might entail authorized or reverse-engineered designs, possibly utilizing foreign technology or parts.
Nonetheless, uncertainties persist regarding the supply chains backing this expansion. Western sanctions and export limitations have sought to curtail Russia’s access to cutting-edge electronics, optical components, and aerospace-quality materials. Although some internal solutions and indirect pathways might alleviate these limitations, the long-term feasibility of mass drone production in such a scenario is doubtful. Experts remain vigilant for indications of how Russia is acquiring essential components and modifying designs to suit accessible materials.
The scale of the expansion also has broader implications for regional and global security. As UAVs become more central to military operations, the ability of one nation to rapidly boost its drone capabilities may prompt others to respond in kind, potentially leading to a wider arms race in unmanned systems. Moreover, the proliferation of drones raises concerns about asymmetric warfare, where even modest investments can yield significant tactical advantages.
From a technological perspective, the video and satellite images disclose a combination of human and machine-driven operations inside the factory. Employees are observed manually putting together parts, yet some sections contain conveyor belts and machine-supported production equipment. This mixed strategy indicates that even though Russia is enhancing its abilities, it might still depend on labor-heavy techniques due to the lack of more advanced manufacturing facilities.
Moreover, besides military factors, the evolution of the site indicates an increasing movement towards incorporating dual-purpose technologies—items and systems that can be utilized for both civilian and defense needs. The drones employed in agriculture, infrastructure analysis, or emergency situations may have similar basic parts to those used in military versions. This convergence makes it more challenging to separate completely commercial production from strictly military production, making it difficult to control or limit the transfer of technology.
The geopolitical context surrounding this expansion cannot be ignored. As global tensions rise and conflicts persist, the development and display of drone manufacturing facilities serve as both a functional necessity and a form of signaling. Russia’s willingness to lift the veil on such a facility—however partially—marks a shift in its public-facing defense posture. It suggests a narrative of self-reliance, industrial capability, and strategic adaptation in the face of international pressure.
International observers, including intelligence agencies and defense think tanks, will likely continue to monitor developments at the site. Regular satellite passes and open-source analysis now play a vital role in tracking military-industrial activity, offering transparency in areas where official information is limited or propagandized.
As the contribution of drones to worldwide conflicts expands, attention towards the supporting infrastructure will increase as well. The progress at Alabuga demonstrates how a nation is addressing this need—via swift building, intentional openness, and an intricate network of logistics that aligns with its objectives. It is yet to be determined how this growth will influence the overall power dynamics in the realm of unmanned systems, and if other countries will intensify their initiatives in reaction.